Why Does Atomic Number Increase Down a Group
Atomic size gradually decreases from left. This increases the pull effect of nucleus resulting in the increase in atomic radius of the atom.

Trends In The Periodic Table Poster By Compound Interest Periodic Table Periodic Table Poster Chemistry Basics
It may also be worth mentioning the atomic radius distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron as this can often be worth a mark on some exam boards.

. Does atomic size increase down the group. Hence the bonds are weaker and less energy is required to break them. Atomic size increases down the group because of the addition of extra shells.
There are two main factors that affect atomic radius. The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. The atomic number increases so does the effective nuclear charge.
This results in an atomic radius that is greater. As the atomic number increases within a period the atomic radius decreases. Correspondingly why does the atomic radius increase down the group.
The growth of nuclear charge pulls more intensely the electrons pulling them closer to the nucleus. Why Does Atomic Size Increase Down A Group. As the number of protons within the nucleus ie.
Effective nuclear charge or Z_eff as this increases the atomic radius decreases the nuclear charge attracts the electrons more towards the nucleus. On coming down the group Number of protons increases nuclear charge increases atomic size decreases. So as we move from group 1 to group 18 the size of the atom will decrease due to increased effective nuclear charge.
This results in a larger atomic radius. As the atomic number increases down a group there is again an increase in the positive nuclear charge. This increases the pull effect of nucleus resulting in the increase in atomic radius of the atom.
The number of energy levels n increases in a group downwards since there is a larger distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital. The valence electrons occupy higher levels due to the increasing quantum number n. This is caused by the increase in the number of protons and electrons across a period.
Each additional shell adds a layer that disrupts the attraction between the protons in the nucleus and the electrons in the shells that pull an atom together. Why does atomic size decreases on moving from left to right across a period even on increasing the atomic number of elements. Why the melting points of the elements decrease down Group 1 and increase down Group 7.
As one moves down the group there is significant jump in the size of the nucleus Protons atomic number Neutrons. The atomic radius increases as you go down a group in the periodic table. And as we move from period 1 to period 7 the size will increase due to increase in shells.
This More electrons mean more shells. Number of shells increases atomic radius increases. The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group.
Also to know is why does atomic radius increase in a group. Why does the ionization energy tend to decrease from top to bottom within a group. The effective nuclear charge Z eff increases down a group which draws electrons closer towards the nucleus decreasing atomic radius.
Why does the size of the elements increase down a group. The shielding effect increases since now electrons from previous shells also contribute to the shielding effect atomic radius increases. Shielding by inner electrons.
The atomic numbers of the elements down a group increase. If this is the case why would the atomic radii increase if theres more nuclear attractive forces going down a group. Why does the atomic size increase down the group.
In general atomic radius. Thus electrons are pulled towards. Atomic size increases down the group because of addition of extra shell.
The atomic radii of atoms increase as you travel down a family on the periodic table because of the increased number of electron shells. Why does the atomic size increase down a group class 10. Looking at group 1 for example it seems that Zeff remains the same at 1 ie the increase in number of shielding electrons is negated by the increase in protons and consequently atomic radii increases.
The additions of new shells increases the distance between nucleus and valance electrons. However there is also an increase in the number of occupied principle energy levels. Down a group the number of energy levels n increases so there is a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital.
One proton has a greater effect than one electron. Larger radius is nothing but larger size. This is because within a period or family of elements all electrons are added to the same shellDown a group atomic radius increases.
The additions of new shells increases the distance between nucleus and valance electrons. Atomic size gradually decreases from left to right across a period of elements. There is an increase in atomic number and atomic size down the group due to addition of extra shellsthis.
As one moves down the group there is significant jump in the size of the nucleus Protons atomic number Neutrons. As the number of electron shells increases down the group and consequently the atomic radii get bigger the attraction between the nuclei and outer shell valence electrons decreases. Atomic size decreases across a Period from left to right as we face the Table but INCREASES down a Group a column of the Periodic TableAnd thus across the Period nucular charge predominates and draws the valence electrons towards the nuclear core with the result of a marked decrease in atomic radius.
Atoms get larger because more electrons are being added in higher energy levels and each energy level is further from the nucleus than the last. Why and how does atomic radius change from top to bottom within a group. As the atomic number increases down a group there is again an increase in the positive nuclear charge.

5 7 Periodic Properties Of The Elements Chemistry Libretexts Element Chemistry Ionic Radius Electron Configuration
What Happens To The Atomic Mass As You Go Down Each Group Family Socratic

Pin By Bhoomi On History In 2021 Atomic Number Meant To Be Positivity

Omg Beautiful Fantastic Revision Notes Revision Notes Chemistry Notes

High School Chemistry Atomic Size Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Periodic Trends In Ionic Radii Chemistry Libretexts Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Element Chemistry

Periodic Properties Of The Elements Electron Affinity Element Chemistry Chemistry Textbook

Trends In The Periodic Table Chpt 7 1 Atomic Radius Size 2 Ionization Energy 3 Electronegativity The Ionization Energy Periodic Table Covalent Bonding

The Periodic Table A Compilation Of Fun Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Education Teaching Chemistry

Trends On The Periodic Table Periodic Table Positive And Negative Ionization Energy

Neon S Melting Point Is 248 67 C Melting Point Boiling Point Atomic Number
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic

Periodic Trends In Electronegativity Ck 12 Foundation Chemistry Periodic Table Ionization Energy Teaching Chemistry

Does Atomic Size Increase Down A Group
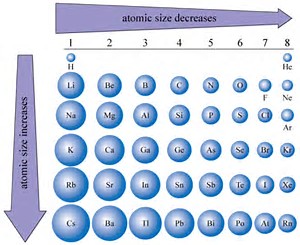
Why Does Shielding Effect Increase Down A Group Socratic

The Periodic Table Lesson Objectives Leveled Books Oxidation State Periodic Table
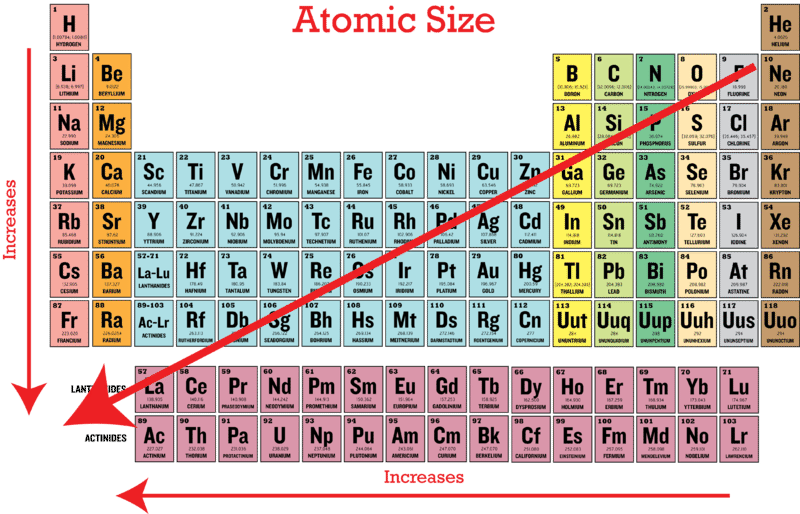
Periodic Trends In Atomic Size Ck 12 Foundation

Atomic Size Size Goes Up On Going Down A Group Ppt Download
Why Does The Atomic Radius Remain Almost Unchanged On The Periodic Table Quora
Comments
Post a Comment